디논실 lab3-4정리
- 5 minsLab 3 실습
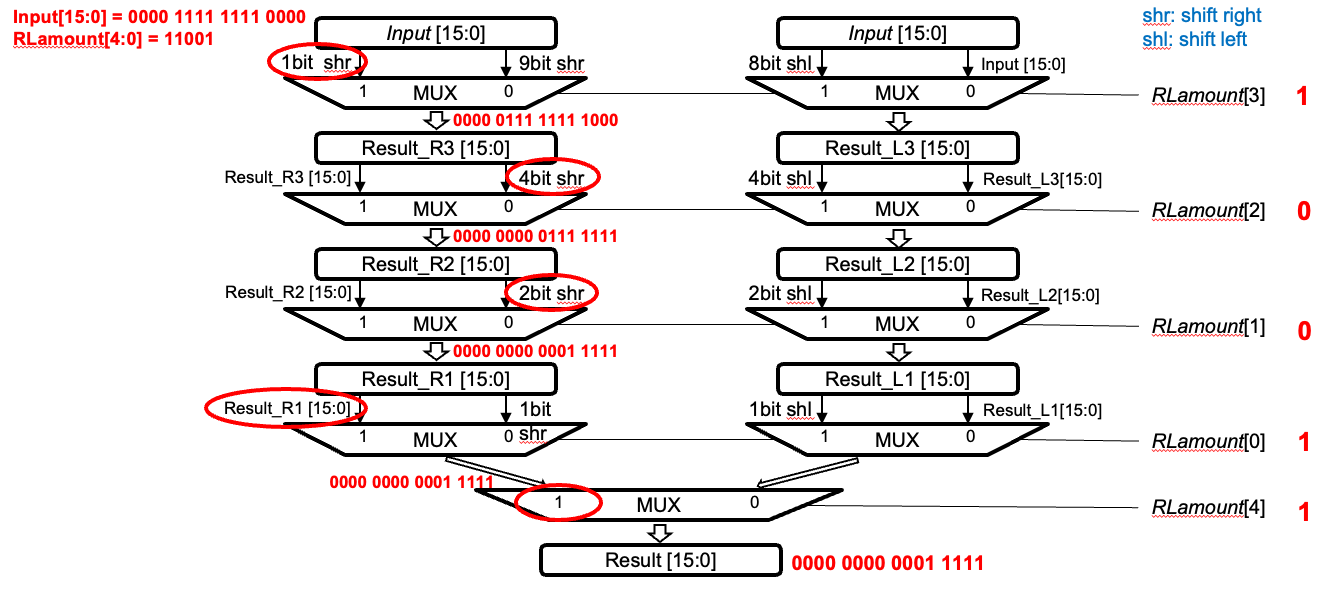
Bi-directional logical shifter
Logical shfit만 고려, MSB나 LSB의 빈자리를 0으로 채움
in: shift 진행할 operand
RLamount : Right, Left amount의 의미인듯? shift할 크기, 2’s complement로 표현
lui : 8bit left shift 여부에 대한 입력
결론적으로 RLamount보다 lui가 항상 우선한다.
RLamount는 MSB를 기준으로 MSB가 1이면 right shift, MSB가 0이면 left shift인데, right shift인 경우 2’s complemnet ( flip + 1 ) 값 만큼 이동
주어진 힌트는 RLamount MSB가 음수인 경우 0인 자리수를 누적해서 계산한 값에 +1만 연산해주면 2’s complement 연산과 같다.
작성한 코드는 다음과 같다.
//// module1: 16bit MUX
module mux16 (
input [15:0] input1,
input [15:0] input0,
input select1,
output [15:0] output1
);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//// TODO: assign MUX's output1
assign output1 = (select1)? input1 : input0;
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
endmodule
//// module2: bi-directional logical shifter
module shifter (
input [15:0] in,
input [4:0] RLamount,
input lui,
output [15:0] out
);
wire [15:0] out1, out2, out3, out4, out5, out6, out7, out8;
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//// TODO: insert parameter
//// for right shift
mux16 mux16_minus_3 (.input1(in>>1),.input0(in>>9),.select1(RLamount[3]),.output1(out1));
mux16 mux16_minus_2 (.input1(out1),.input0(out1>>4),.select1(RLamount[2]),.output1(out2));
mux16 mux16_minus_1 (.input1(out2),.input0(out2>>2),.select1(RLamount[1]),.output1(out3));
mux16 mux16_minus_0 (.input1(out3),.input0(out3>>1),.select1(RLamount[0]),.output1(out4));
//// for left shift
mux16 mux16_plus_3 (.input1(in<<8),.input0(in),.select1(RLamount[3]),.output1(out5));
mux16 mux16_plus_2 (.input1(out5<<4),.input0(out5),.select1(RLamount[2]),.output1(out6));
mux16 mux16_plus_1 (.input1(out6<<2),.input0(out6),.select1(RLamount[1]),.output1(out7));
mux16 mux16_plus_0 (.input1(out7<<1),.input0(out7),.select1(RLamount[0]),.output1(out8));
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//// TODO: assign shifter's output
assign out = (lui)? in<<8 : ((RLamount[4])? out4: out8);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
endmodule
assign 문과 submodule을 적절히 활용할 수 있는 좋은 예시인 것 같다. wire 변수를 활용해서 assign을 활용해볼 수 있는 좋은 예시. assign statement는 combinational logic에서 사용된다.
combinational logic 과 sequential logic의 가장 큰 차이는 sequential logic의 경우 출력값이 이전 입력들의 영향을 받는다는 것이다.
개인적으로 lui값이나 RLamount값도 multiplexer를 사용할 수 있으니 그렇게 skeleton code를 주는것도 나쁘지 않다고 생각한다.
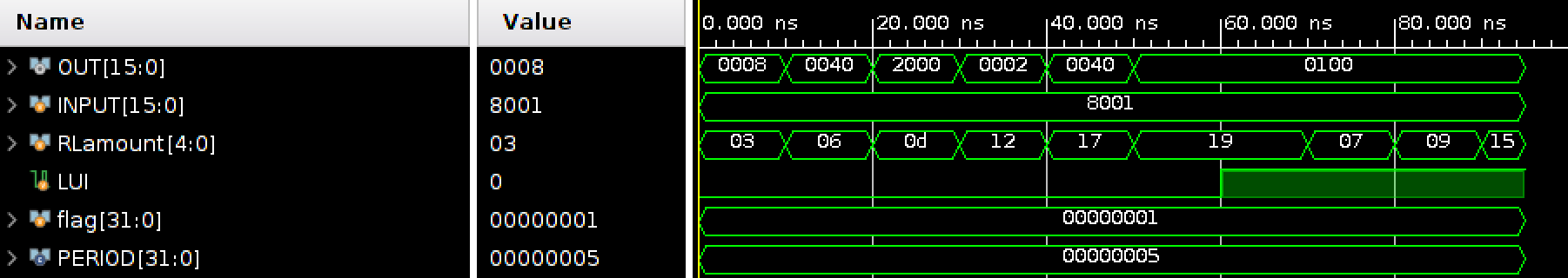
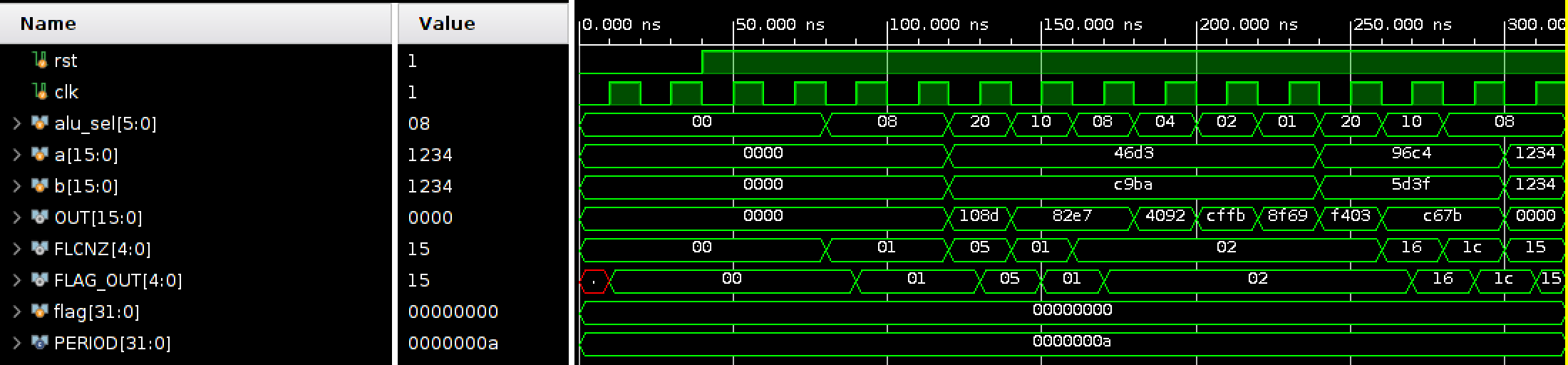
Simulation result
ALU & PSR( Program Status Register )
ALU
alu_sel가 선택한 산술/논리 연산을 수행한다. out = A (op) B 를 수행하면 되고 flcnz의 경우 연산 결과에 대한 상태를 저장해야한다.
flcnz 의 spec은 다음과 같다.
- F flag: signed number 의 OF output
- L flag: unsigned number의 C flag, CMP 연산 시 A>B 여부 확인
- C flag: unsigned number의 OF
- N flag: Signed number의 CMP 연산 확인, C flag xor A[15] xor B[15]
- Z flag: SUB 연산 결과 0인지 여부, B-A의 연산 결과의 모든 bit에 대한 NOR 연산
N flag가 조금 특이한데, 만약 Signed number의 A>B가 true 인 경우
Z flag는 ?
산술 연산의 경우 Carry Lookahead Adder(CLA) 모듈을 활용하면 된다.
CLA 모듈 input/output spec은 다음과 같다. 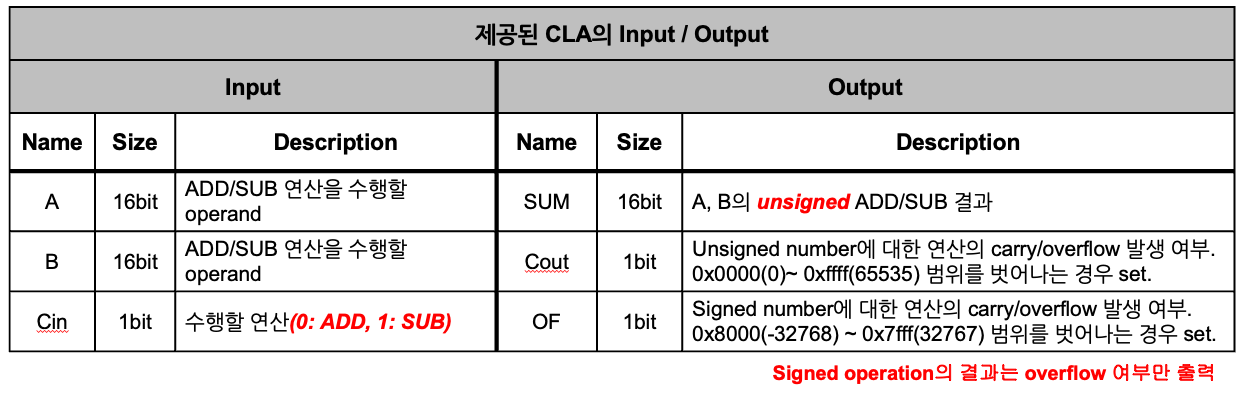
PSR
- ADD, SUB일때 F, C flag 업데이트
- CMP일때, L, N, Z flag 업데이트
Implementation code
module ALU (
input [15:0] A,
input [15:0] B,
input [5:0] alu_sel,
output reg [15:0] out,
output reg [4:0] flcnz
) ;
reg c_in;
wire Cflag,Fflag,Zflag,Nflag,Lflag;
wire [15:0] sum;
wire [15:0] cmp, and1, or1, xor1;
integer i;
reg nor_val;
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//// TODO: insert right value for adder
CLA_16Bit cla16 (
.A(A),
.B(B),
.C_in(c_in),
.S(sum),
.C_out(Cflag),
.OF(Fflag)
);
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
always @(*) begin
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//// TODO: insert value to "c_in" using case statement
case (alu_sel)
6'b100000 : c_in = 0;
6'b010000 : c_in = 1;
6'b001000 : c_in = 1;
6'b000100 : c_in = 0;
6'b000010 : c_in = 0;
6'b100001 : c_in = 0;
endcase
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
end
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//// TODO: insert flag values
//assign and1 = ;
//assign or1 = ;
//assign xor1 = ;
assign Zflag = nor_val ;
assign Lflag = Cflag;
assign Nflag = Cflag ^ A[15] ^ B[15];
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//// TODO: insert value to "FLCNZ" and "out"
always @(*) begin
case (alu_sel)
6'b100000: begin // ADD
//// flags from fc, out = some value
flcnz[4] = Fflag;
flcnz[2] = Cflag;
out = sum;
end
6'b010000: begin // SUB
//// flags from fc, out = some value
flcnz[4] = Fflag;
flcnz[2] = Cflag;
out = sum;
end
6'b001000: begin // CMP
//// flags from lnz
flcnz[3] = Lflag;
flcnz[1] = Nflag;
flcnz[0] = Zflag;
out = sum;
nor_val = sum[0];
for(i=1; i < 16; i= i+1)begin
nor_val = ~(sum[i] | nor_val);
end
end
6'b000100: begin // AND
//// out = some value
out = A & B;
end
6'b000010: begin // OR
//// out = some value
out = A | B;
end
6'b000001: begin // XOR
//// out = some value
out = A ^ B;
end
default: begin
flcnz = 5'b0;
out = 16'b0;
end
endcase
end
endmodule
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Simulation result
고쳐야 할 부분
- PSR을 왜쓰는지 설명해주면 좋을 것 같다.
- FLCNZ flag들이 43210에 대응한다는 설명 추가
- CMP도 A-B 결과값을 이용한다는 것을 분명히 명시
- PSR pseudo code에는 특정 flag만 업데이트하라는 듯이되어있는데 그게 아니라 통채로 업데이트
- Signed shifter로 구현하게 하면 쉽게 변형가능할듯하다.
- PSR 구현 왜 필요한지 잘 모르겠음.
Lab 4 실습 : Traffic Light Controller 설계
issue
- 굉장히 불친절
Code
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//// TODO: insert your codes about (n_state)
always @(*) begin
case(c_state)
3'b000 : begin
if (HS == 1'b0 && FS == 1'b0) n_state = 3'b000;
else n_state = 3'b001;
end
3'b001 : begin
if (HS == 1'b1) n_state = 3'b010;
else if ( FS = 1'b1) n_state = 3'b011;
else n_state = 3'b001;
end
3'b010 : begin
if (HS == 1'b1) n_state = 3'b100;
else n_state = 3'b010;
end
3'b011 : begin
if (FS == 1'b1) n_state = 3'b101;
else n_state = 3'b011;
end
3'b100 : begin
if (FS == 1'b0) n_state = 3'b110;
else n_state = 3'b011;
end
3'b101 : begin
n_state = 3'b111;
end
3'b110 : begin
n_state = 3'b000;
end
3'b111 : begin
n_state = 3'b000;
end
endcase
end
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
미팅 결과
=> FSM 주차 맞추기 => Lab1/Lab2 합치기 Test bench 1개 통과
PPT랑 변수이름 mapping
shift가 op코드가 아니다.
RISC processor: 사진 최신으로 바꾸기
Lab3, Lab4 순서 고려해보기 ( pyQt? )
코드에 맞춰서 HGREEN ->.